Compressed fluid-based technology platform for biomaterials processing
Scientific leaders: Prof. Nora Ventosa & Prof. Jaume Veciana
Coordinators: Dr Gemma Martinez and Dr. Nathaly Segovia
Industrial problem/gap covered
The conventional approaches used for the production of particulate molecular biomaterials usually follow easy preparation methods at the laboratory scale, but they fail when scaling-up to industrial level.
Description
NANBIOSIS approach offers novel synthetic strategies and experimental setup for the advanced preparation of a wide range of nanoparticles, including inorganic and soft nanoparticles with biomedical application. An example is CF-based methodology which presents several advantages including the reduction of organic solvent use, low working temperatures, few operational steps and easy scale-up for the preparation of uniformly structured materials with precise and reproducible structural characteristics at micro-, nano- and supramolecular levels. Furthermore, CF-based methods have been shown to be suitable processes for the one-step preparation of polymeric micro- and nanoparticles and nanovesicles for the delivery of therapeutic entities with increased bioavailability, efficacy, stability and selectivity.
In the development of this biomedical solution, the following services are involved:
Nanovesicles like Quatsomes
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 |
Nanovesicles like Quatsomes |
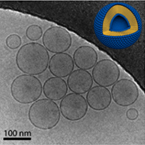
– Nanovesicular systems composed by sterols and cationic surfactants.
– Size in the nano-range (below 100nm) – Uniform shapes (spherical and unilamellar)
– Highly Monodisperse
– Long-term stability (up to one year)
– Antimicrobial and antifungal properties |
– Drug Delivery Systems (DDS) for both pharmaceuticals (Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), etc.) and biopharmaceuticals (proteins, DNA, RNAs, etc.)
– Entrapment of dyes, stabilizing and targeting moieties.
Ref:
1. New nanodrug improves the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (http://www.dicat.csic.es/rdcsic/index.php/en/biologia-y-biomedicina-2/108-histories-d-exit/310-una-nanomedicina-mejora-la-regeneracion-de-las-ulceras-de-pie-diabetico), Patent WO 2014/019555 A1.
2. Multifunctional Nanovesicle-Bioactive Conjugates Prepared by a One-Step Scalable Method Using CO2-Expanded Solvents, Nano Letters, DOI: 10.1021/nl4017072. |
Nanovesicles like Liposomes
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 |
Nanovesicles like Liposomes |
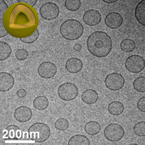
– Nanovesicular systems composed by sterols and phospholipids
– Size in the nano range (below 200nm)
– Monodisperse
– Uniform shapes (spherical and unilamellars)
– Short-term stability (1 month) |
– DDS for both pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals.
– Entrapment of dyes, stabilizing and targeting moieties.
Ref:
1. Multifunctional Nanovesicle-Bioactive Conjugates Prepared by a One-Step Scalable Method Using CO2-Expanded Solvents, Nano Letters, DOI: 10.1021/nl4017072. |
PEGylated Nanovesicles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 |
PEGylated Nanovesicles |
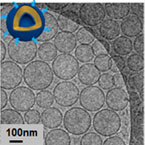
– PEGylated nanovesicular systems
– Size in the nano range (below 100 nm)
– Highly Monodisperse
– High Uniform shapes (spherical and unilamellar)
– Long term stability (up to one year) |
– DDS for both pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals, with high stability due to the functionalization with hydrophilic poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG), a stealth agent used to prolong blood-circulation time while reducing mononuclear phagocyte system uptake.
– Entrapment of dyes and targeting moieties.
Ref:
1. Multifunctional Nanovesicle-Bioactive Conjugates Prepared by a One-Step Scalable Method Using CO2-Expanded Solvents, Nano Letters, DOI: 10.1021/nl4017072 |
Polymeric particles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 |
Polymeric particles |
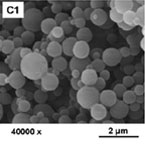
– Polymeric Nanoparticles composed by biocompatibles polymers, such as PVP, GANTREZ, EUDRAGIT, PEG, CYCLODEXTRINES.
– Size in the micro, submicron, and nano range
– Monodisperse
– Uniform shapes |
-DDS for both pharmaceuticals (APIs, anticancer drugs,etc.)
Ref:
1. High Loading of Gentamicin in Bioadhesive PVM/MA Nanostructured Microparticles Using Compressed Carbon-Dioxide, Pharm Res (2011), DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0248-x
2. Novel bioactive hydrophobic gentamicin carriers for the treatment of intracellular bacterial infections, ActaBiomaterialia (2011), DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.11.031 |
Solid fine particles of APIs
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 |
Solid fine particles of APIs |

– Fine particles of APIs
– Size in the micro range
– Narrow size distribution
– High crystallinity degree
– High polymorphic purity
– Free of residual solvents |
– To increase the bioavailability and dissolution rate of pharmaceuticals
– To allow the use of a more appropriate and/or convenient administration route, such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, topical and intestinal modes of administration
Ref:
1. Crystallization of Microparticulate Pure Polymorphs of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Using CO2-Expanded Solvents, Cryst. Growth Des. (2012), DOI: 10.1021/cg200356x |
Hollow Au Nanoparticles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Hollow Au Nanoparticles |
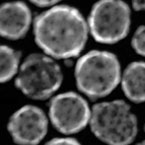
Gold nanoparticles with spherical shape and average diameters ranged between 60-80 nm |
Application: Photothermal therapy and thermally induced gene expression
Ref:
– RSC Adv., 2016,6, 58723-58732.
– Biomaterials, Volume 35, Issue 28, September 2014, Pages 8134-8143
– Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, Volume 9, Issue 5, July 2013, Pages 646-656 |
Au Magnetic /SiO2nanoshellwith a spions located inside
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Au Magnetic /SiO2nanoshellwith a spions located inside |
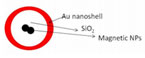
Magnetic nanoparticles in the core, covered by a shell of SiO2 with an external layer of gold, and average diameter of 100 nm |
Application: Photothermal therapy and MRI signaling (theranosticnanoparticles)
Ref:
– Nanoscale. 2014 Aug 7;6(15):9230-40. |
Hollow Au nanoshell with a spion located inside
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Hollow Au nanoshell with a spion located inside |
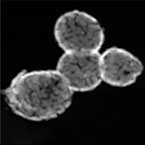
Magnetic Gold-based nanoparticles with magnetic and optical properties. Spherical shape and average diameter of 150 nm |
Application: Photothermal therapy and MRI signaling (theranostic nanoparticles)
Ref:
– Nanoscale. 2014 Aug 7;6(15):9230-40. |
Au NPs capped with citrate
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Au NPs capped with citrate |
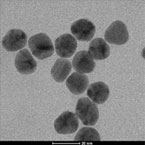
Gold nanoparticles with average diameters of 20 nm |
Application: Transfection reagent
Ref:
– ActaBiomaterialia, Volume 7, Issue 10, October 2011, Pages 3645-3655 |
Au nanorods capped with lysine
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Au nanorods capped with lysine |
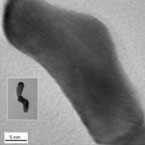
Gold-based nanorods |
Application: Contrast agents for optical coherence tomography
Ref:
– ChemCommun (Camb). 2012 Jul 7; 48(53): 6654–6656 |
Au nanorods capped with citrate
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Au nanorods capped with citrate |

Gold-based nanorods |
Application: Photothermal therapy
Ref:
– Materials Research Bulletin, Volume 48, Issue 10, October 2013, Pages 4051-4057 |
CuS nanoparticles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
CuS nanoparticles |

Copper sulfide nanoparticles with an average diameter of 150 nm |
Application: Photothermal therapy
Ref:
– ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Aug 24;8(33):21545-54. |
Hollow CuS nanoparticles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Hollow CuS nanoparticles |

Sulphur/copper hollow nanoparticles with an average diameter of 200 nm |
Application: Photothermal therapy
Ref:
– ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Aug 24;8(33):21545-54. |
Carbon nanodots
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Carbon nanodots |
Carbon-based nanoparticles with spherical shape and average diameters ranged between 2-6 nm |
Application: Bioimaging in the UV-Vis-Near Infrared ranges
Ref:
Chem. Eur. J. 10.1002/chem.201604216 |
Magnetic nanoparticles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Magnetic nanoparticles |
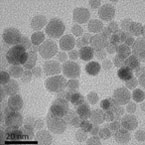
Iron-based nanoparticles with spherical shape and average diameters ranged between 6 -13 nm |
Application: MRI diagnosis (T2 contrast agents)
Ref:
J Nanopart Res (2014) 16:2292 |
PLGA nanoparticles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
PLGA nanoparticles |
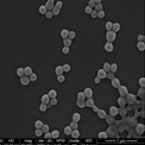
|
Application: drug delivery
Ref:
– ActaBiomater. 2017 Mar 1;50:493-501.
– RSC Adv., 2016,6, 111060-111069 |
Polymeric nanoparticles with an Au nanoparticles inside
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U9 |
Polymeric nanoparticles with an Au nanoparticles inside |
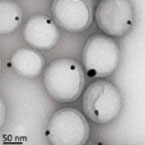
|
Application: Drug delivery and contrast agents (theranostics)
Ref:
Nanoscale, 2016,8, 6495-6506 |
Peptide-targeted Nanovesicles
| Unit |
Type of NP |
Specifications of the NP (Size, composition, etc) |
Applications & reference |
| U6 with collaboration of U3 |
Peptide-targeted Nanovesicles |
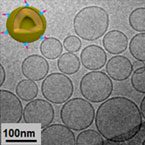
– Nanovesicular systems composed by sterols and phospholipids
– Size in the nano range (below 200nm)
– Monodisperse
– Uniform shapes (spherical and unilamellar)
– Short-term stability (2 months) |
– DDS for both pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals, with high stability due to the functionalization with an RGD targeting peptide. – “Active targeting” through the incorporation of specific molecules on the outer surface of nanovesicles, which can provide more effective therapeutic action to a nanomedicine, due to a more specific and effective cellular uptake.
Ref:
1. α-Galactosidase A Loaded Nanoliposomes with Enhanced Enzymatic Activity and Intracellular Penetration, Nano Lett., 2013, DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500746 |
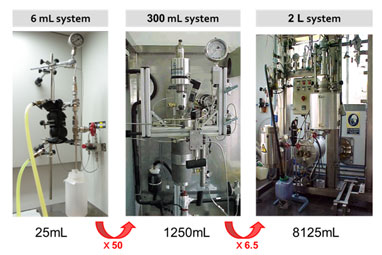 |
It gathers several laboratories, perfectly equipped, to perform the mission of this facility: the development, characterization, and large-scale production of molecular biomaterials of therapeutic or biomedical interest, with controlled micro-, nano- and supramolecular structure. One example of Key-Enabling-Technology (KET) available in this unit is a simple one-step methodology, DELOS-SUSP, based on the use of compressed fluids (CF), such as CO2, to prepare particulate materials with precise and reproducible structural characteristics at micro-, nano- and supramolecular levels (size, shape, internal structural gradients, supramolecular organization and crystalline purity).This example shows one of the singularities of this unit is that counts with CF–based plants at different scales, from mL to L, which allow process development by QbD and process scale-up.
|
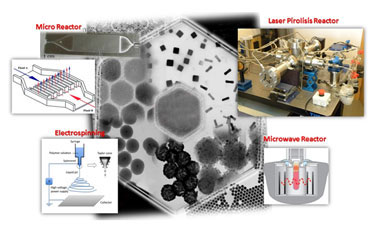 |
This unit offers novel synthetic strategies and experimental setup for the advanced preparation of a wide range of nanoparticles, including inorganic and soft nanoparticles with biomedical application.
The new methodologies include microreactors, laser pyrolysis reactor and electro spinning. Both laser pyrolysis and microreactors as belonging to the group of enabling technologies, which allow new goals in reproducibility and scale-up production of nanomaterials. As for the electro spinning, this is a new infrastructure that allows the preparation of nanowires and fibres, formed by different materials.
|



















